Remote Procedure Call (RPC) dynamic port allocation is used by server applications and remote administration applications such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Manager, Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) Manager, and so on.
Basically, the automation of this article.
https://support.microsoft.com/kb/154596?wa=wsignin1.0
I've added this at Script Center.
Please download at https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/RPC-Port-Allocation-using-7f1c52c1.
Search This Blog and Web
Tuesday, November 11, 2014
Tuesday, October 21, 2014
SQLCMD.exe in SQL Server 2012 does not give real-time output logging
I hit into an another issue in SQL 2012 related to real-time logging.
I've logged bug here : https://connect.microsoft.com/SQLServer/feedback/details/1002565
The problem is when a long running Stored Procedure is run using sqlcmd.exe of SQL Server 2012, the output is not displayed in real-time. It gets displayed only after the query completes or user stops it.
In SQL Server 2008's sqlcmd.exe, the output is displayed as-is without any delay.
Workaround : The behaviour is not there in OSQL.exe.
Since Microsoft wants us to use sqlcmd.exe in place of osql.exe, I think this thing should be fixed.
Please vote-up.
I've logged bug here : https://connect.microsoft.com/SQLServer/feedback/details/1002565
The problem is when a long running Stored Procedure is run using sqlcmd.exe of SQL Server 2012, the output is not displayed in real-time. It gets displayed only after the query completes or user stops it.
In SQL Server 2008's sqlcmd.exe, the output is displayed as-is without any delay.
Workaround : The behaviour is not there in OSQL.exe.
Since Microsoft wants us to use sqlcmd.exe in place of osql.exe, I think this thing should be fixed.
Please vote-up.
Labels:
2012,
connect,
osql,
sql server,
sqlcmd
[Script] Get Disk Space using PowerShell
I posted a simple script at Technet which returns the free space of a specific drive on any computer.
Take a look here : https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Get-Disk-Space-using-69c88b59
Basic Code :
The script can be improved using PS-Remoting for better performance.
Take a look here : https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Get-Disk-Space-using-69c88b59
Basic Code :
Write-Host "Getting Information for Drive : $DriveID for Computer : $CompName" # Get Info about the disk specified $Disk = Get-WMIObject Win32_LogicalDisk -ComputerName $CompName -Filter "DeviceID='$DriveID'" $FreeSpace = [System.Math]::Round((($Disk.FreeSpace) / 1GB)) Write-Host "Drive $DriveID has freespace : $FreeSpace GB"
The script can be improved using PS-Remoting for better performance.
Labels:
powershell,
script,
technet,
wmi
Thursday, April 10, 2014
[TOOL] SQL Service Account password change/update (multiple servers)
Today, I'm going to share a tool that I've developed for changing password of SQL service account on (n) servers.
Background : Typically in an organisation as a best-practice account password is changed every 90 days(to prevent brute-force attack's success). Many Windows services are run using these accounts. Hence, there password needs to be updated.
Manual Way : Take a remote desktop connection to the server, open services.msc, select service and update password in Logon tab.
This is fine for 1 or 2 servers but this process does not scale-up in an enterprise where there are many servers and also many services are being run on each server(like sqlserveragent,ssis,ssas,ssrs).
Background : Typically in an organisation as a best-practice account password is changed every 90 days(to prevent brute-force attack's success). Many Windows services are run using these accounts. Hence, there password needs to be updated.
Manual Way : Take a remote desktop connection to the server, open services.msc, select service and update password in Logon tab.
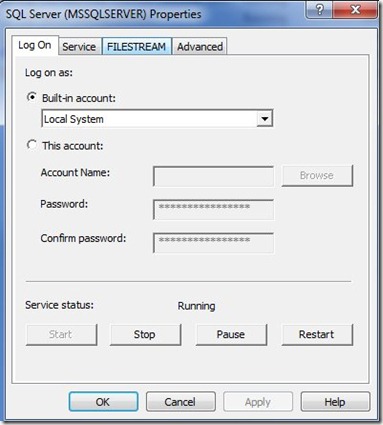 |
| Src : http://www.sqlservercentral.com/blogs/steve_jones/2011/12/15/how-to-change-the-sql-server-service-cccount/ |
Automation : As always, Power Shell is there to the rescue. There are two methods to achieve that 1. SMO 2. WMI
I first tried using SMO but it broke at crucial point. (Avoid SMO as far as you can.)
So, the second option with me was WMI.
Basically, all SQL services are Windows services and can be managed using Win32_Service class.
Basic Code :$service = gwmi win32_service -computer [computername] -filter "name='whatever'"
$service.change($null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,"P@ssw0rd")
Full Code :
# Script should be run on systems having PowerShell V3 installed.
# Run PowerShell as ADMINISTRATOR.
# Remoting must be enabled on destination servers using "Enable-PSRemoting -Force"
# In case of errors, please try running this command on local machine : gwmi win32_bios -comp "server1" where "server1" is the machine for which you get error. This should run fine for utility to proceed.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Service Account Password Change
.DESCRIPTION
Power Shell utility to change password of SQL service account on (n) servers
.PARAMETER Path
$servers : List of Server(s) separated by comma
$AccountName : Name of the account through which service is running and whose password needs to be changed
.EXAMPLE
cd "E:\Utilities\ServiceAccount";
.\SQLServiceAccount.ps1 -Servers "s1","s2" -accountName "redmond\v-any"
.NOTES
Author: r1111111r@gmail.com
Date : 15/01/2014
Version : 1.0
You must be having access to the servers.
This should be run only from systems having PowerShell V3. Destination servers may have V2/V3.
.INPUTS
List of servers and account name
Then password when prompted
.OUTPUTS
On Screen and file-logging.
It logs into the directory from which it's invoked/called.
#>
param(
[cmdletBinding()]
# Seprate list by commas eg. "ser1","ser2"
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string[]] $servers,
# eg. "domain\account"
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [ValidatePattern("(\w+)\\(\w+)")]
[string] $accountName
)
# Bail-out in case of any error
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
# Generic helper function
function ConvertTo-ScriptBlock
(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string] $ScriptString
)
{
$ScriptBlock = $ExecutionContext.InvokeCommand.NewScriptBlock($ScriptString)
Return $ScriptBlock
}
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
# Look up this script file's path
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
# This function writes the input Msg into the console window
function Log
(
[string] $Msg = $(throw "Msg parameter not specified!")
# Define the foreground color in which to log; if not specified, default provided
,[string] $Fore = "cyan"
)
{
Write-Host (Get-Date -format "yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss") $Msg `n`r -fore $Fore
}
Log "Account specified is $accountName"
# Get password from the user and store it as a "Secure String"
# UserName, Message parameters are available only in V3
$pass = (Get-Credential -UserName $accountName -Message "Enter password for account")
If($pass -eq $null) {Log "Password not specified"; throw}
# get alias name from domain\alias e.g. domain\alias will return alias
$account = ($accountName.Split("\")[1])
$path = (Get-ScriptDirectory)
if(!(Test-Path $path)) {Log "Invalid log path $path" -Fore Red ; throw}
# Checks whether Transcript is in progress
function Test-Transcribing {
$externalHost = $host.gettype().getproperty("ExternalHost",
[reflection.bindingflags]"NonPublic,Instance").getvalue($host, @())
try {
$externalHost.gettype().getproperty("IsTranscribing",
[reflection.bindingflags]"NonPublic,Instance").getvalue($externalHost, @())
} catch {
Write-Warning "This host does not support transcription."
}
}
# The function that stops services (including dependent services), changes password & starts them again
function Change-ServiceAccount()
{
# This is the code to fetch the services for SQL server including SSIS, OLAP
$services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "DisplayName LIKE '%SQL%'"
Write-Host "Total SQL services are : " ($services.Count)`n`r
foreach($service in $services)
{
Write-Host "Processing service : " $service.Name`n`r
# Need services that are run by the account specified
if($service.StartName -match "$account")
{
$serviceName = $service.Name
Write-Host "Service is running under : " $service.StartName`n`r -ForegroundColor Yellow
Log "Stopping service : $serviceName"
# Stop All services so that "Dependent Services" are not running
# It's better and simpler than $service.Stop() as the later does not stop dependent services by default
Get-Service -Name $serviceName | Stop-Service -Force -Verbose
Log "Changing password for $serviceName"
# uint32 Change(DisplayName,PathName,ServiceType,ErrorControl,StartMode,DesktopInteract,StartName,StartPassword,LoadOrderGroup,LoadOrderGroupDependencies,ServiceDependencies);
$RetCode = $service.Change($null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$pass)
# Get error message from return code
$msg = RetCodes -Code ($RetCode.ReturnValue)
if($RetCode.ReturnValue -ne 0) { throw "Error : $msg" }
Start-Sleep 2
Log "Starting service : $serviceName"
$RetCode = $service.StartService()
$msg = RetCodes -Code ($RetCode.ReturnValue)
if($RetCode.ReturnValue -ne 0) { throw "Error : $msg" }
}
else
{
Write-Host "Skipping Service : " $service.Name `n`r -ForegroundColor White
}
}
}
# These are the list of return codes of Change() function which changes password
function RetCodes ([int] $Code)
{
switch ($Code)
{
0 { "Success" }
1 { "Not Supported" }
2 { "Access Denied"}
3 { "Dependent Services Running"}
4 { "Invalid Service Control"}
5 { "Service Cannot Accept Control"}
6 { "Service Not Active"}
7 { "Service Request Timeout"}
8 { "Unknown Failure"}
9 { "Path Not Found"}
10 { "Service Already Running"}
11 { "Service Database Locked"}
12 { "Service Dependency Deleted"}
13 { "Service Dependency Failure"}
14 { "Service Disabled"}
15 { "Service Logon Failure"}
16 { "Service Marked For Deletion"}
17 { "Service No Thread"}
18 { "Status Circular Dependency"}
19 { "Status Duplicate Name"}
20 { "Status Invalid Name"}
21 { "Status Invalid Parameter"}
22 { "Status Invalid Service Account"}
23 { "Status Service Exists"}
24 { "Service Already Paused"}
default {"Invalid return code"}
}
}
# Make function calls from here
try
{
# Read local function
$RetFunction = (Get-Content Function:\RetCodes)
$RetFunction = "Function RetCodes {" + $RetFunction + "}"
$RetScriptBlock = (ConvertTo-ScriptBlock -ScriptString $RetFunction)
$LogFunction = (Get-Content Function:\Log)
$LogFunction = "Function Log {" + $LogFunction + "}"
$LogScriptBlock = (ConvertTo-ScriptBlock -ScriptString $LogFunction)
#Create log file to store execution result
$StartTime = Get-Date -Format "yyyyMMdd_hhmm"
$logFile = "$path\ServiceAccount_$StartTime.log"
Start-Transcript $logFile
foreach( $server in $servers)
{
# Check Server is valid and alive
Log "Testing Connection to $server"
If(Test-Connection -ComputerName $server -Quiet)
{
Log "Creating Connection to $server"
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName $server
If($session.State -eq "Opened") { Log "Successfully connected to : $server" -Fore "Yellow"}
# Create function RetCodes in remote session
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock $RetScriptBlock
# Create function Log in remote session
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock $LogScriptBlock
# Pass local variable to remote session
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock {param($account)} -ArgumentList $account
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock {param($pass)} -ArgumentList $pass.GetNetworkCredential().Password
# Call local function in remote session
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock ${function:Change-ServiceAccount}
}
else
{
Log "Server : $server is not valid/available, skipping it" -Fore "Red"
}
}
}
catch
{
Write-Host "oops! " $Error[0] `n`r -ForegroundColor Red
Write-Host "Please check `"http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa384901(v=vs.85).aspx`" for error details"
#Start-Process "http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa384901(v=vs.85).aspx" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
finally
{
Log "Clearing Sessions" -Fore "Yellow"
Get-PSSession | Remove-PSSession
if(Test-Transcribing) { Stop-Transcript }
}
Important Points : The above script is optimized using remoting and is amazingly fast. If you need a quick short version, only read and use Change-ServiceAccount function.
At the end, thanks to the all the people whose information I've used in creating this utility. Please let me know your comments on this.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Featured Post
Timeout problem in Backup-SQLDatabase cmdlet in SQLPS module
Power Shell is for managing all types of technologies be it SQL, EXchange, Lync, Office etc.( just name it ) These technologies usually cr...